The problem of cybercrime keeps manifesting in different folds as technology keeps advancing, digital devices are embedded in the way of life of the people, and internet penetration keeps soaring without cyberspace protection. This development has raised concerns and necessitated a cybersecurity conversation. Cybersecurity is paramount to economic development considering the huge damages that cybercrime imposes on individuals, businesses, institutions, and governments, which transcend from monetary loss to reputational loss, and loss of investors. The push for the digitalization of economies has been globally recognized, and as state institutions and governments are assiduously implementing it, avenues are widening for cybercrime activities, which has further created problems emanating from these initiatives. A look at how securing cyberspace drives economic development.
Fraser, (2020) posits that the global economy is dependent on technology and driven by digital infrastructure. Technological innovations coupled with cyber security help businesses pursue their value chain activities and turn a profit for their owners and shareholders. Securing cyberspace makes it more conducive and hygienic for businesses to thrive. At the rate at which businesses are moving online and exploiting technological systems, securing cyberspace appears to be indispensable. The profits and expansion witnessed within the business space among both private and state-owned businesses in the digital economy are attributed to the protection of cyberspace. This, by extension, means that without cyber security, the growth of the digital economy would be halted, truncated, or unhygienic. This is evident in the report by Ramachandran (2019) that global e-commerce is growing at a phenomenal rate, as 1 billion consumers were expected to make purchases across borders in 2020 (compared to 390 million in 2016), per the Global E-commerce Association.
Oxford Economics (2016) argued that cyber security is more than just an “insurance policy” against hackers, malware, or other threats. They opined that agile, proactive cybersecurity capabilities could help drive growth and innovation. It is thought that a solid cybersecurity foundation is necessary for effective digital transformation. On this basis, businesses will feel secure using digital procedures and technologies that stimulate innovation and expansion. For instance, the paperless port system, which has been implemented in Ghana, contributed to a 3.9% increase in import revenue (from 12.7 billion to ¢ 13.2 billion) from 2017 when it was first implemented, to 2018 in just a year of implementation. Without it, companies may hesitate to start digital projects, stifling their innovation potential and opening the door to digital disruptors. This shows cyber security drives economic development, especially in the digital economy; by making cyberspace hygienic, businesses will be motivated to implement processes and technologies that bring growth and development.
Cybercrime is estimated to have caused damages totaling US$6 trillion globally in 2021, as the statistics from Cyber Security Ventures indicate. The amount is argued to be twice the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of all African countries combined (Media Foundation for West Africa, 2022). In the case of Ghana, from 2016 to 2022, $271.8 million was lost to cybercriminals, according to statistics from the Cybercrime Unit of the Criminal Investigative Department of the Ghana Police. Businesses, organizations, institutions, individuals, and governments incur these losses. Cybercrime is also projected by Cybercrime Magazine to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. These monies could have been invested in the global and local economies of the respective countries for economic expansion. In essence, not protecting cyberspace costs the world a huge sum of money through the activities of cybercriminals. What this suggests is that, aside from encouraging businesses to adopt technologies to develop and grow their businesses, monies that could have been lost to cyber criminals would be invested in an economy like Ghana’s to propel economic growth. $19.8 million is a huge sum of money that, when invested in a sector, would have a positive impact on the Ghanaian economy.
Cybersecurity drives economic development in the sense that securing cyberspace is an incentive for foreign investors. When cyberspace is secured from attacks, foreigners are motivated to invest in businesses in such a country. When established, these businesses will pay taxes, employ graduates, and increase the country’s GDP. In most cases, these businesses undertake social responsibilities in their host country, which contributes to the development of the country. This argument is supported by a report by CyberSource Corp., a payment processor in the United States, that in 2008, over half of US merchants who accepted international orders refused to process purchases from Ghana, citing fraud concerns (Motiwala, 2017). This would not encourage investors in the credit and payment systems to invest in Ghana, which hinders the growth of local credit and payment systems. Conversely, secured cyberspace would invite investors in the credit and payment systems to Ghana.
Having identified the impact of digitalization on the economy of a country, it is safe to say cyber security contributes to economic development, by creating a conducive and hygienic environment for digitalization to thrive. As mentioned earlier, in the case of Ghana, as a result of cyber security, the government has implemented a lot of digitalization policies that have contributed to economic growth and the ease of doing business in the country. The paperless port system alone witnessed an import revenue increase of 3.9% (from 12.7 billion to ¢ 13.2 billion) from 2017 to 2018 (Wass, 2019). In the Mobile Money market, MTN mobile money also witnessed 9% year-on-year growth in the first half of 2022 (The Business & Financial Times, 2022). These were achieved partly as a result of the interventions made in the area of cyber security in the country. The information and communication subsector has also witnessed huge growth. This is due to the various cyber security measures being implemented that have offered the players in the sector the opportunity to introduce technological innovations, leading to growth in the sector and a huge contribution to the Gross Domestic Product of Ghana, especially in the year 2020. Below are some excerpts from the telecommunications sector’s contribution to the Ghanaian economy.
Figure 1: Telecom sector contribution to Ghana’s GDP 2020
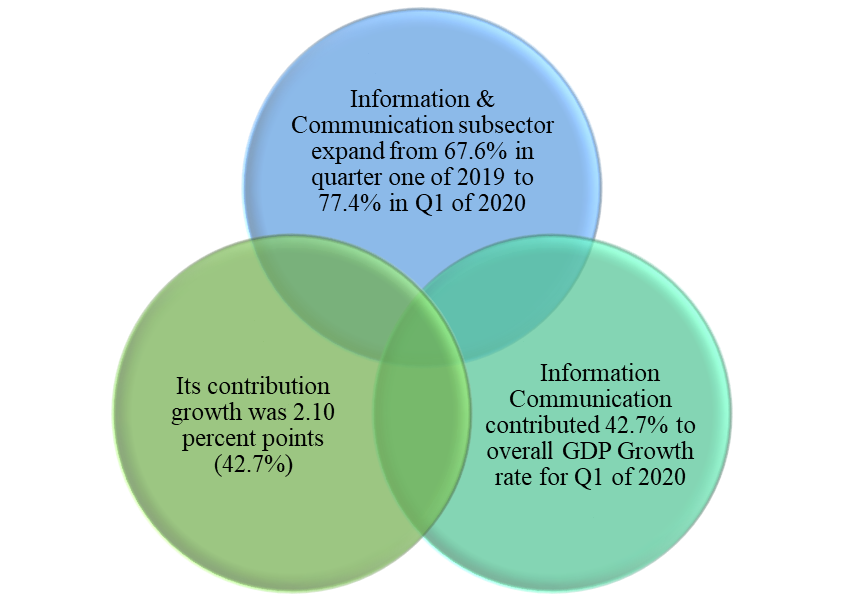
Source: Ghana Statistical Service, 2020.
The discussions brought up above clearly show that cyber security is a potent tool that, when used correctly, may spark a significant economic revolution and, eventually, progress. In addition to fostering economic growth, securing the cyber space would place the nation among those nations excelling in cyber security (international recognition that has a knock-on impact on development as well).
Author’s Profile: Abdul-Salam Shaibu is an Investigator and Cybersecurity Practitioner. [PhD (Candidate), P-G Law (UK), MSc, BSc, Dip.] Ghana, UK. The author’s research interests are in IT, Cybersecurity, Law, Risk Management, Security, and Criminal Psychology.
Recommended Citation: Abdul-Salam, S. (2023). How Cybersecurity Drives Economic Development.
Please address all correspondence to: Abdul-Salam Shaibu by Phone: at (+233) 026 530 8783 and by email on shaibubaba80@gmail.com


